PowerShell is an automation platform and scripting language developed by Microsoft for simplifying and automating the management of Windows and Windows Server systems. PowerShell users can access PowerShell through a command-line shell or the PowerShell Integrated Scripting Environment (PowerShell ISE).
- Task automation framework
- Command line shell
- Scripting language
- .Net framework
- Both local and remote
- Access to com and WMI
Access the Command-Line Interface :-
- Click on Windows Power Screen from the Start screen or task bar.
- Run PowerShell as an administrator:
- Right-click Windows PowerShell in the Start screen or task bar.
- Click Run as Administrator.
1.Get-Help
For example:-If you want to know how the Get-Process command works, you can type:Get-Help -Name Get-Process or Get-Help -Name Get-*
2. Set-ExecutionPolicy
For example:- If you wanted to allow scripts to run in an unrestricted manner you could type:
Set-ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted
3. Get-ExecutionPolicy
For example:- execution policy is in use before you attempt to run a script.
4. Get-Service
For example:-Windows will show you the service's state.
Get-Service | where (All running service) Get-Service | where {$-.status -eq 'running'
5. Select-Object
For example:- Get-Service | Select-Object Name, Status | Export-CSV c:\arun.csv
6. Get-Process
For example:- Get-Process command to display a list of all of the processes that are currently running on the system.
Get-Process (display all running process)Get-Process s* (start with s)
7. Stop-Process
For example:- you could terminate Notepad by using one of the following commands:Stop-Process - Name notepad | stop (stop notepad)Stop-Process -ID 2684
8. Export-CSV
For example:- Get-Service | Export-CSV c:\arun.csv
9. ConvertTo-HTML
For example:- Get-Service | ConvertTo-HTML -Property Name, Status > C:\arun.htm
10. Get-EventLog
For example:- to see the Application log, you could use the following command:
Get-EventLog -LogName 'DNS server' Get-EventLog -LogName 'DNS server' -After "4/8/18"
Windows PowerShell Pipeline(|):-
- Pipeline provides a way for us to filter out every things.
- Separator of two command (get-services and where -object) filtering ,grouping ,shorting etc.
- Pipe and is the character above the backslash on your keyboard.
- Pipeline Symbol (|) or (¦)
For example 1:-
Get-Process notepad | Stop-Process
For example 2:-
get-process chrome | format-list
Benefit of being Object Oriented:-Object Oriented Programming has great advantages over other programming styles:
Code Reuse and Recycling: - Objects created for Object Oriented Programs can easily be reused in other programs
Encapsulation -Part 1:- Once an Object is created, knowledge of its implementation is not necessary for its use. In older programs, coders needed understand the details of a piece of code before using it (in this or another program).
Encapsulation -part 2:- Objects have the ability to hide certain parts of themselves from programmers. This prevents programmers from tampering with values they shouldn't. Additionally, the object controls how one interacts with it, preventing other kinds of errors. For example, a programmer (or another program) cannot set the width of a window to -400.
Display Features and Roles through Windows server in PowerShell :-
Get-WindowsFeature :-Display a list of the features and roles on our server.
Syntax:- Get-WindowsFeature
Syntax:-Get-WindowsFeature | where {$_.InstallState -eq "Installed"}
Get-WindowsFeature -ComputerName Server123 | Where InstallState -Eq Removed (Display a list of features on a specified server, Server123, that have installation files removed from the local side-by-side store)
Install-WindowsFeature:-
Syntax:- Install-WindowsFeature -Name <feature_name> -computerName <computer_name> -Restart
OR
Install-WindowsFeature -Name <feature_name> -VHD <path> -computerName <computer_name> -Restart
For example:- Install-WindowsFeature NET-Framework-Core -Source E:\Sources\AxA
Uninstall-WindowsFeature:-
Syntax:- Uninstall-WindowsFeature -Name <feature_name> -computerName <computer_name> -Restart
OR
Uninstall-WindowsFeature -Name <feature_name> -VHD <path> -computerName <computer_name> -Restart
For example:-Uninstall-WindowsFeature -Name Web-Server -ComputerName Server123 -Credential contoso\user123
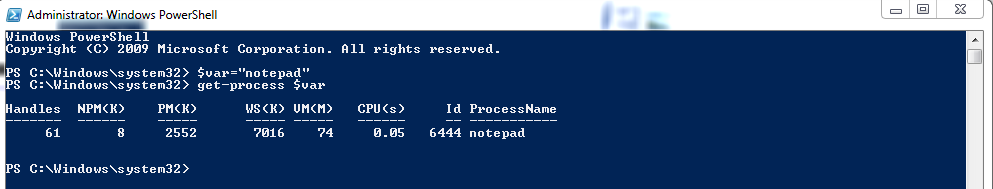
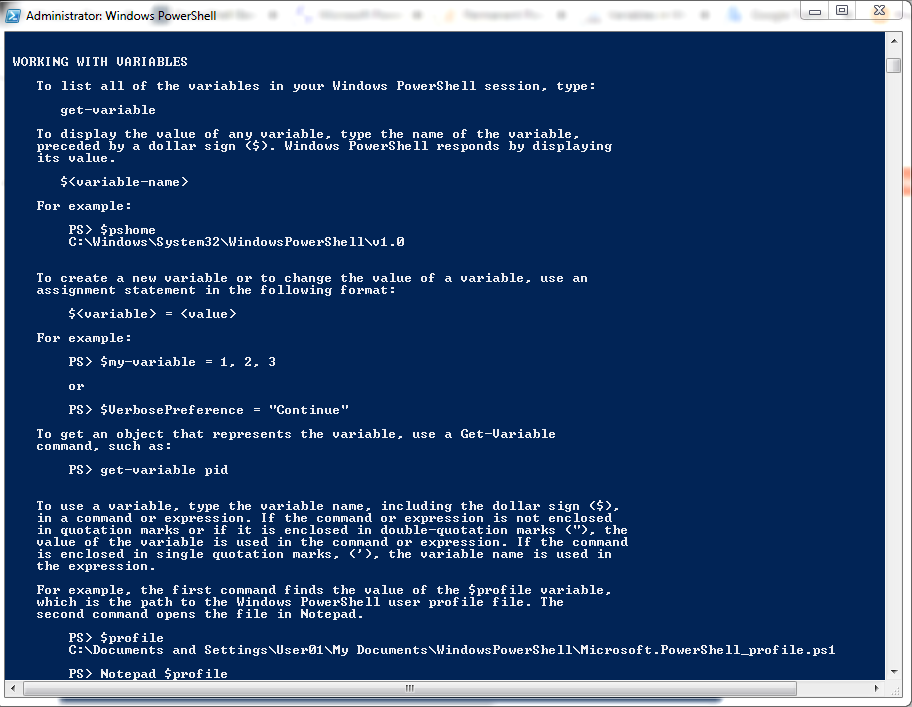
Power of Variables in Windows PowerShell:-
variable names always start with a dollar sign ($) and can contain a mix of letters, numbers, symbols, or even spaces (though if you use spaces, you need to enclose the variable in braces, such as ${My Variable} = "https://pyarungupta.blogspot.com").
Syntax:- $var = "https://pyarungupta.blogspot.com"
Assigning and Referencing PowerShell Variables:-
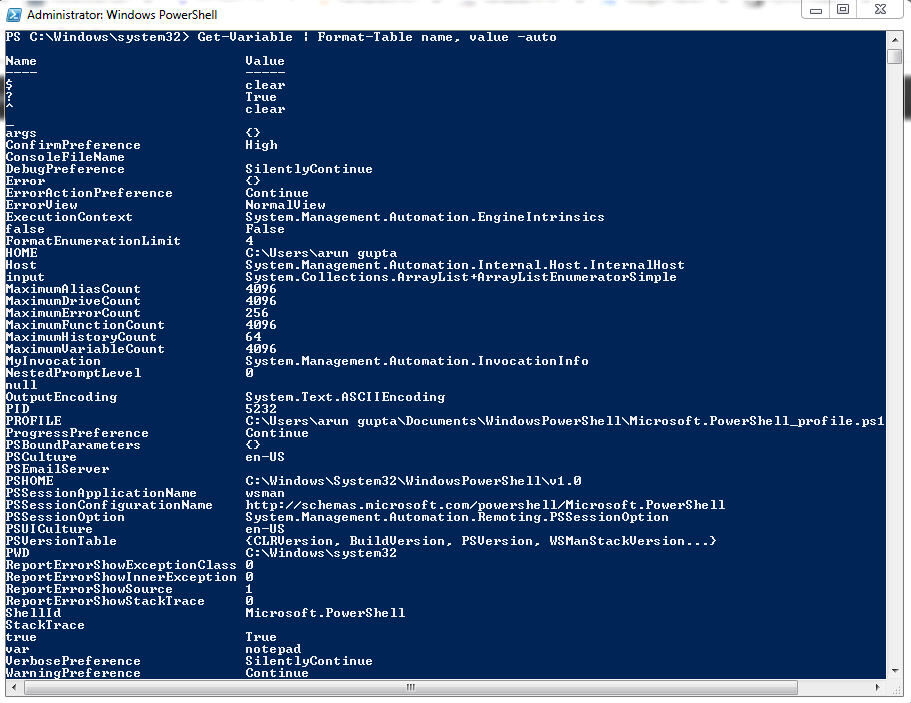
Built-In PowerShell Variables:-
Syntax:- Get-Variable | Format-Table name, value -auto
Name
|
Description
|
$_
|
The
current pipeline object; used in script blocks, filters, the process clause
of functions, where-object, for each-object and switch
|
$^
|
contains
the first token of the last line input into the shell
|
$$
|
contains
the last token of last line input into the shell
|
$?
|
Contains
the success/fail status of the last statement
|
$Args
|
Used in
creating functions that require parameters
|
$Env:Path
|
Environmental
Path to files.
|
$Error
|
If an
error occurred, the object is saved in the $error PowerShell variable
|
$foreach
|
Refers
to the enumerator in a foreach loop.
|
$HOME
|
The
user's home directory; set to %HOMEDRIVE%\%HOMEPATH%
|
$Input
|
Input
piped to a function or code block
|
$Match
|
A hash table consisting of items found by the -Match operator.
|
$MyInvocation
|
Information
about the currently script or command-line
|
$Host
|
Information
about the currently executing host
|
$LastExitCode
|
The
exit code of the last native application to run
|
$PSVersionTable
|
Chech
the version of PowerShell
|
$true
|
Boolean
TRUE
|
$false
|
Boolean
FALSE
|
$null
|
A null
object
|
$PsUnsupported
ConsoleApplications |
List unsupported commands
|
$OFS
|
Output
Field Separator, used when converting an array to a string.
By default, this is set to the space character. |
$ShellID
|
The
identifier for the shell. This value is used by the shell to determine
the Execution Policy and what profiles are run at startup.
|
$StackTrace
|
contains
detailed stack trace information about the last error
|
Types of variables in Windows PowerShell:-
Syntax:-Get-Help about_Variable
- about_Automatic_Variables
- about_Environment_Variables
- about_Preference_Variables
- about_scopes
Working with Variables:-
1. Display installed Antivirus Name in PowerShell
Syntax:-
$Antivirus_test = "SELECT * FROM AntiVirusProduct"
$Win_Antivirus_Test
= gwmi -Namespace "root\SecurityCenter2" -Query $Antivirus_test @psboundparameters
write-host
$Win_Antivirus_Test.displayname
Result: -
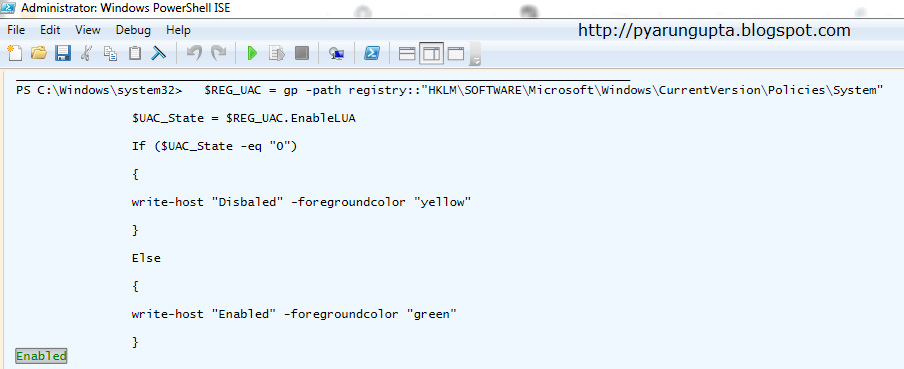
2. Display UAC status in PowerShell
Syntax:-
$REG_UAC
= gp -path
registry::"HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System"
$UAC_State
= $REG_UAC.EnableLUA
If
($UAC_State -eq "0")
{
write-host
"Disbaled" -foregroundcolor "yellow"
}
Else
{
write-host
"Enabled" -foregroundcolor "green"
}
Result :- Enabled
3. Display default printer in PowerShell
3. Display default printer in PowerShell
Syntax:-
$Win32_Printer
= gwmi -Query " SELECT * FROM Win32_Printer WHERE Default=$true"
write-host
$Win32_Printer.name
Result: -PR00165777
4. Display installed language packs
Syntax:-
$Win32_OperatingSystem
= gwmi Win32_OperatingSystem
write-host
$Win32_OperatingSystem.MUILanguages
1. 5.Display
Windows defender status
Syntax:-
$Test_Win_Defender
= Get-Service -DisplayName 'Windows Defender'
If
($Test_Win_Defender.Status -eq "Stopped")
{
write-host
"Disbaled" -foregroundcolor "yellow"
}
Else
{
write-host
"Enabled" -foregroundcolor "green"
}
6. Display Firewall status
Syntax:-
$Firewall_state
= $REG_Firewall.EnableFirewall
If
($Firewall_state -eq "0")
{
write-host
"Disbaled" -foregroundcolor "yellow"
}
Else
{
write-host
"Enabled" -foregroundcolor "green"
}
7. Display installed RAM
Syntax:-
$Win32_ComputerSystem
= gwmi Win32_ComputerSystem
$Memory_RAM
= [Math]::Round(($Win32_ComputerSystem.TotalPhysicalMemory/ 1GB),1)
write-host
$Memory_RAM + "GB"
8. List of Hard drive
Syntax:-
$Win32_LogicalDisk
= get-wmiobject Win32_LogicalDisk | where {$_.DriveType -eq "3"}
#---------------
Disk informations : deviceid, totalsize; freespace #---------------
ForEach
($disk in $Win32_LogicalDisk) ### Enum Disk
{
$Total_size
= [Math]::Round(($disk.size/1GB),1)
$Free_size
= [Math]::Round(($disk.Freespace/1GB),1)
$Disk_information
= $Disk_information + "(" +
$disk.deviceid + ") " + $Total_size + " GB Total / " + + $Free_size + " GB Free `n"
}
$Disk_information
Result: -
(D:) 97.7 GB Total / 45.8 GB Free
9. Display the current Time zone
Syntax:-
$Win32_TimeZone
= gwmi Win32_TimeZone
write-host
$Win32_TimeZone.Caption
10. Display Internet Explorer version
Syntax :-
$REG_IE
= gp -path registry::"HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Internet Explorer"
$IE_Ver=
$REG_IE.svcUpdateVersion + " (" + $REG_IE.svcKBNumber + ")"
write-host
$IE_Ver
Syntax:-
$REG_SCCM
= get-itemproperty -path registry::"HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\SMS\Mobile
Client"
write-host
$REG_SCCM.AssignedSiteCode
Result: -SD1





















Nice and knowledgeable article.good
ReplyDeleteThank for watching vijay ji
ReplyDeleteThank you all for your valuable comments .
ReplyDeleteThank you all for your valuable comments .
ReplyDeleteThanks for visiting our blog website.
ReplyDelete