 Python is a general purpose high level programming language and dynamically type programming language.Most easiest programming language.
Python is a general purpose high level programming language and dynamically type programming language.Most easiest programming language. First language :-
 >>>print ("hello word" )
>>>print ("hello word" ) hello word
>>> a, b=10,20
>>> print(a+b)
30
>>>a=10
>>> type(a)
int
When we can use python:-
- Desktop Application
- Web Application
- Database Application
- Network Application
- Games
- Data Analysis
- Machine Learning
- Artificial Intelligence
- Internet of Things (IoT) Application
- Google (YouTube)
- Facebook (Tornado)
- Dropbox.
- Yahoo.
- NASA.
- IBM.
- Mozilla.
- Simple and easy to learn
- Free ware and open source
- High level programming language
- Platform Independent(write One and run any where)
- Portability
- Dynamically Type
- Both procedure oriented and Object oriented
- Interpreted
- Extensible
- Embedded
- Extensive Library
Flavors of the Python programming language:-
- Cpython ( For C language)
- Jpython ( For Java Platform )
- IronPython ( for C#,.net Platform )
- Pypy (Just-in-time compilation )
- RubyPython (for Ruby Platform )
- Anaconda Python ( For Big data)

1.Alphabet systems (uppercase (A to Z) and lowercase (a to z) )
digits (0 to 9) or an underscore (_)
For example:-Cash=20 allow
C@sh=20 not allow
2.Identifier show not starts with digit
For example:- total12=20
12total=20 not valid
3.Identifier are case sensitive
For example:- total=20
TOTAL=20
4.Max length of python identifiers No length of python identifiers (no limit)
For example:-xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx=10
- (_) Private (Start with Underscore)
- (__) Strangle private (Two under score)
- (____) Main(social variable in create python)
Reserved words:- ( 33 Keywords )
>>> import keyword
>>> keyword.kwlist
['False', 'None', 'True', 'and', 'as', 'assert', 'break', 'class', 'continue', 'def', 'del', 'elif', 'else', 'except', 'finally', 'for', 'from', 'global', 'if', 'import', 'in', 'is', 'lambda', 'nonlocal', 'not', 'or', 'pass', 'raise', 'return', 'try', 'while', 'with', 'yield']
>>>
Note:- Only alphabet symbols start capital latter (True,False, None) except three all lowercase.
Data Types:- ( 14 Types)
1 .int
For example:- x = 10
2. float
For example:- x = 45.67
3. complex
For example:- x = 3.14J
4. bool
For example:- True or False
True+ True=2; False+True=1; True/True=1; True/False=Error
5. String :- uses single quotes ' double quotes " and triple quotes """ to denote literal strings.
For example:- firstName = 'Arun' lastName = "Gupta"
message = """Multi line string literals"""
6. List:-A list can contain a series of values. List variables are declared by using brackets [ ]
- General purpose
- Most widely used data structure
- Useful for variable data
For example:-
X = [ ] # This is a blank list variable
Y = [1, 2, 3, 4] # this list creates an initial list of 4 numbers.
Z = [2, 4, 'Arun'] # lists can contain different variable types.
7. Tuple:-The fixed size is considered immutable as compared to a list that is dynamic and mutable. Tuples are defined by parenthesis ().
- Immutable(can't add/change)
- Useful for fixed data
- Faster than lists
For example:-
xyz = ('Arun', 'Gupta', 'baraunsa', 'sultanpur')
Note:- Advantages and Disadvantages depends upon the use. If you have such a data which you never want to change then you should have to use tuple, otherwise list is the best option.
8. Dictionary:-Its are lists of Key:Value pairs and created by using braces ({}) with pairs separated by a comma (,) and the key values associated with a colon(:).
For example:-
xyz = {'Arun': 200, 'Gupta': 100}
9. Bytearray:-
For example:-
10. Range:- range data type represent a sequence of value immutable.
For example:- r=range(10) it represents value 0 to 9
>>>range(10,20,2) ==> increment of 2==>10,12,14..
11. Set:-Moreover, no duplicate elements can be present.
For example:-
12. Frozenset:-
For example:-
13. None:-
For example:-
14. Bytes:-
For example:-
Note:- long :-python 3 not available
Slice Operator:- Extracts
elements, based on a begin and end.
- Begin- starting integer where the slicing of the object starts
- End - integer until which the slicing takes place. The slicing stops at index end - 1.
- Step - integer value which determines the increment between each index for slicing
For example: - S= “arungupta”
S[1:5]==> 1to 4==> ‘ rung’
S[1:5:2]==> ‘rn’
Most important loops and control Statements in python:-
Selection Statements:- Selection statement provides the means of choosing between two or more paths of execution.
- If
- If ..else
- If..elif…else
For example :-
if n1>n2 and n1>n3
Print (“”)
elif n2>n3:
Print (“”)
Else:
Print (“”)
Repetition Statements:-The repeated execution of a statement or compound statement is accomplished either by iteration or recursion.
- while loop:-Repeat things till the given number of times.
For example 1 :- x=1
While x<=1
Print(x)
X+=1
For example 2:- x=0
While true:
X=x+1
Print(“arun”)
- for loop:-Repeat things until the loop condition is true.
Do some action
S= “arungupta”
For x in s:
Print(x)
Transfer statements:-
Break:-Base on some condition if we want to break look execution.
For example :-WAP to prints current latter
for letter in 'arunguptapython':
# break the loop as soon it sees 'a' or 'n'
if letter == 'a' or letter == 'n':
break
print 'Current Letter :', letter
Result:-Current Letter : a
Continue:-Base on some condition if we want to continue look execution.
For example :-WAP to prints all letters except 'a' and 'n'
for letter in 'arunguptapython':
if letter == 'a' or letter == 'n':
continue
print 'Current Letter :', letter
var = 10
Result:-
Current Letter : r
Current Letter : u
Current Letter : g
Current Letter : u
Current Letter : p
Current Letter : t
Current Letter : p
Current Letter : y
Current Letter : t
Current Letter : h
Current Letter : o
Pass:-pass is a keyword in python
it is an empty statement.
it is null statement.
it won't do anythings.
if True:
else:
print("arunguptapython")
Errors:
Result:- No Output
if True:pass
else:
print("arunguptapython")
For example :- WAP to prints last letter.
for letter in 'arunguptapython':pass
print 'Last Letter :', letter
Result:-
Last Letter : n
Iterators, Iterables, Generators, Containers, Decorators and Closures in Python:-
Iterators:-It is create our own iter() and next() methods and only one element is stored in the memory at a time.For example, an odd number iterator currently at 3 returns the next odd number of 5.
For example:-

Iterables :-An iterable is any object, not necessarily a data structure, that can return an iterator
For example:-
Here, x is the iterable, while y and z are two individual instances of an iterator.
Generators:- It is a sequence of values and generator in python makes use of the ‘yield’ keyword.
We can say every generator is an iterator in python, not every python iterator is a generator.
Syntax:-
def even(y):
while(y!=0):
if y%2==0:
yield y
y-=1
for j in even(8):
print(j)
Two types of Generators :-
Generator functions:-It is any function in which the keyword yield appears in its body.
Generator expressions:-it is equivalent to list comprehension.
For example:-
OR
sum([y*y for y in range(1,10)])
Containers:-Containers are data structures holding elements.They are data structures that live in memory, and typically hold all their values in memory.
For examples:-
- list, deque
- set, frozensets.
- dict, defaultdict, OrderedDict, Counter.
- tuple, namedtuple.
- str
Decorators:-It is way to dynamically add some new behavior to some objects
For example:-
>>> def my_deco(func):
... def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
... print("Before")
... result = func(*args, **kwargs)
... print("After")
... return result
... return wrapper
...
>>> @my_deco
... def add(a, b):
... "Our add function"
... return a + b
...
>>> add(1, 3)
Before
After
4
Closures:-It is nothing but functions that are returned by another function. We use closures to remove code duplication.
For example:-
>>> def add_number(num):
... def adder(number):
... 'adder is a closure'
... return num + number
... return adder
...
>>> a_10 = add_number(10)
>>> a_10(21)
31
>>> a_10(34)
44
>>> a_5 = add_number(5)
>>> a_5(3)
8
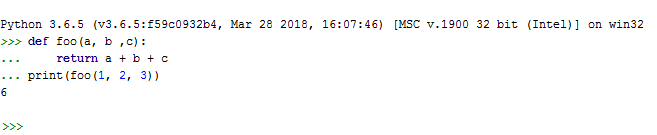
Importance of functions in Python:-
- Reduce the length of code and improve readability.
- Very complex problem we can solve very easily.
- Pass function argument another function in python.
- Reducing duplication of code and Information hiding in python
- Decomposing complex problems into simpler pieces
- Improving clarity of the code and reuse of code in python
- Function can pass parameter and return value in python
- Return multiple value(used tuple)
- Default return value is none.
- Function is start by the "def " statement followed by the function name and parentheses ( () )
- The code within every function begin with a colon (:) and should be indented (space)
Important Parameters Types in Python:-
Default Arguments :- default return value is none.
The default value is assigned by using assignment (=) operator.
The default argument is passed automatically and appears in the
output of the function call.
Syntax:-
OUTPUT:- Arun welcome to here!
Keyword Arguments :- When invoking a
function, inside the parentheses there are always 0 or more values, separated
by commas.
Syntax:-
here a="b" , c=11 keyword parameter and a="arun", c=10 are keyword
argument.
Positional Arguments:- A positional argument is any argument that's
not supplied as a key=value pair.
because
first we a will get value 1 and then we are treating it as keyword argument and
providing extra value which is 3 now a have two values
a=1 which
is positional value
a=3 which is keyword value
a=3 which is keyword value
Variable Arguments:-
*args and **kwargs in Python
We use *args and **kwargs as an argument when we are unsure about the number of
arguments to pass in the functions.
1.*args (Non Keyword Arguments):-
Passes variable length non keyword argument to function using *args.
- *args passes variable number of non-key word arguments list and on which operation of the list can be performed.
Output:-
Sum: 17
Sum: 17
Sum: 35
- **kwargs (Keyword Arguments):-
Passes variable length non keyword argument to function using *args but we cannot use this to pass keyword
argument. For this problem Python has got a solution called **kwargs, it allows us to pass the variable length of
keyword arguments to the function.
- **kwargs passes variable number of keyword arguments
dictionary to function on which operation of a dictionary can be
performed.
Output:-
Place=delhi
FName=Arun
Mname=kumar
Lname=gupta
Address=sultanpur
More example:-
OUTPUT:-

Most Important Functions in Python:-
output:-
uniform():-
syntax:-uniform (x,y)
For example:-
from random import *
for i in range (20):
print(uniform(1,10))
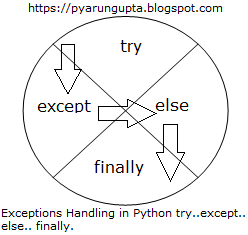
Exceptions Handling in Python -try..except.. else.. finally:-
Python Database Programming (PDB):- it’s very common requirement to save data for the future purpose.
 Tips & Tricks to write better python:-
Tips & Tricks to write better python:-
1.Simplify if statement:-
4.Transposing
a Matrix:-
>>> import itertools

Most Important Functions in Python:-
Built-in Function:-
abs() all() any() basestring() bin() bool()
bytearray() callable() chr() classmethod() cmp() compile()
complex() delattr() dict() dir() divmod() enumerate()
eval() exec() execfile() file() filter() float()
format() frozenset() getattr()
User-defined Function:-User-defined function are reusable code blocks;
they only need to be written once, then they can be used multiple times. They can
even be used in other applications, too.
Syntax:-
def userDefFunction (arg1, arg2, arg3 ...):
program statement1
program statement3
program statement3
....
return;
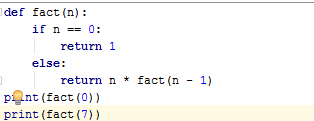
Recursive Function:-A function that call itself recursive function
Syntax:-
factorial (n)=n* factorial (n-1)
For example:-
factorial (3)=3* factorial (2)
The termination condition: n == 0
The reduction step where the function
calls itself with a smaller number each time: factorial (n - 1)
Output:-
1
5040
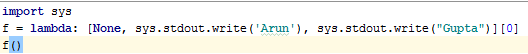
Lambda Expression Function:-
syntax for lambda:- lambda <args>:
<expression>
Output:-
GuptaArun
Multiple things inside a lambda:-
Filter():-filter function check same filter
Syntax:- filter(function, Sequence)
Output:-
[2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
Map():- Pass multiple iterables to the map function
like list, dictionary, etc.
Syntax:-
map(function, iterable1, iterable2, iterable3...)
Output:-
[2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22]
Reduce():-It used a rolling computation to sequential pairs of values
in a list. It returns a single value.
Syntax:- reduce(function, Sequence)
Output:-
10
45
Anonymous Function:-Without
nameless function call anonymous function.
Syntax:-
lambda arguments : expression
Output:-
8
10
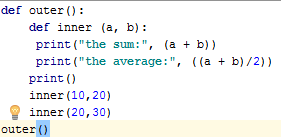
Nested functions:-One function to call another function in same
function.
Write one used multiple time.
Syntax:-
def
outerfunctin(x):
def innerfunction():
print(x)
innerfunction()
outerfunctin(1)
Output:-
the sum: 30
the average: 15.0
the sum: 50
the average: 25.0
Decorators function:-New functionality look existing functions is
already there.
Syntax:-
Output:-
hi Gupta good morning
Variables in Python:- variable is a reserved memory location to store values.
Local Variables:- you want to use the
variable in a specific function or method, you use a local variable.
Global Variables:- you want to use the same variable for
rest of your program or module you declare it a global variable
For Example:-
Output:-
503
pyarungupta.blogsport.com
503
module :-
- A group of functions and variables saved to a file.
- Code reusability.
- Length of the code will be reduced and readability maintainability.
Syntax:- Import module 1
Import module 1, module 2, module 3
Import module 1 as m1 (aliasing modules)
Reloading a module:-module loaded only one time.
Finding member of a module by using dir() function
dir():-current module member
['BPF', 'LOG4', 'NV_MAGICCONST', 'RECIP_BPF', 'Random',
'SG_MAGICCONST', 'SystemRandom', 'TWOPI', 'WichmannHill',
'_BuiltinMethodType', '_MethodType', '__all__',
'__builtins__', '__doc__', '__file__', '__name__',
'__package__', '_acos', '_ceil', '_cos', '_e', '_exp',
'_hashlib', '_hexlify', '_inst', '_log', '_pi', '_random',
'_sin', '_sqrt', '_test', '_test_generator', '_urandom',
'_warn', 'betavariate', 'choice', 'division',
'expovariate', 'gammavariate', 'gauss', 'getrandbits',
'getstate', 'jumpahead', 'lognormvariate', 'normalvariate',
'paretovariate', 'randint', 'random', 'randrange',
'sample', 'seed', 'setstate', 'shuffle', 'triangular',
'uniform', 'vonmisesvariate', 'weibullvariate']
Working with math module:-
Define several functions for math operation
randint():-randint(1,100) (inclusive)
For example:-
output:-
uniform():-
syntax:-uniform (x,y)
For example:-
from random import *
for i in range (20):
print(uniform(1,10))
randrange (start , stop, step):-start <= x < stop
randrange (10) generate a number from 0 to 9
randrange (1,11) generate a number from 1 to 10
randrange (1,11,2) generate a number (1,3,5,7,9)
Exceptions Handling in Python -try..except.. else.. finally:-
try :- Enters at the top and continues through the block
except :- Jump to there is an exception is thrown
else:- Run after the try block completes without exception
thrown
finally :- Always run after the other blocks have completed
- try block compulsory we should write either except or finally block.
- except without try is invalid.
- finally without try is invalid
- we can take multiple except blocks for the same try but we cannot take multiple .
- else without except is invalid.
- try.. except.. else ...finally order is important.
- Nesting of try...except... else... finally is passable.
- Try without except or finally is always invalid.
- Without try except is always invalid.
try:
Risky code
except:
Will be executed if exception in try
else:
Will be executed if no exception in try
finally:
Will be executed always whether exception raised or not raised and handled or not handled.
Invalid and valid
............................valid
try:
print("try")
finally:
print("finally")
..............................valid
try:
print("try")
except:
print("except")
...................................valid
try:
print("try")
except:
print("except")
else:
print("else")
.................................Invalid
try:
print("try")
else:
print("else")
........................................Invalid
try:
print("try")
else:
print("else")
finally:
print("finally")
....................................Invalid
try:
print("try")
except:
print("except")
finally:
print("finally 1")
finally:
print("finally 2")
.........................................Invalid
try:
print("try")
except:
print("except")
print("except 1")
finally:
print("finally")
......................................Invalid
try:
print("try")
except:
print("except")
try:
print("try")
else:
print("else")
................................Invalid
try:
print("try")
try:
print("try1")
except:
print("except")
finally:
print("finally")
....................................................
Predefined exception (Inbuilt exception):- The exception
which is raised automatically by python whenever a particular event occurs.
For example:-
Print (10/0) zero division error
x=int ("ten") value error
User defined exception (Customized exception):-
For example:-Invalid coupon code exception
def recharge(number):
if number is not valid:
raise invalid coupon code exception
We use -import pickle
Pickling and unpickling in Python (serialization, marshalling,
or flattening):-
Pickling:- It is the process whereby a Python object
hierarchy is converted into a byte stream.
- Pickling is just serialization
- Pickling in python refers to the process of serializing objects into binary streams.
- convert the relevant state from a python object into a string.
- Pickling is a way to convert a python object (list, dict, etc.) into a character stream.
- pickle module has an optimized cousin called the cPickle module
- pickle has two main methods. The first one is dump, which dumps an object to a file object and the second one is load, which loads an object from a file object.
Syntax:- Pickle: Pickle.dump (object,file)
Unpickling:- It is
the inverse operation, whereby a byte stream is converted back into an object
hierarchy.
- Unpickling is the inverse of Pickling.
- convert the string to a live object.
- Unpickling is just deserialise
Syntax:-Unpickling: Pickle.load (file)
For example:-
import Pickle
class emp:
def __init__(self,empid,empname):
self.empid=empid #constructor
self.empname=empname
def display(self):
print(self.enpid,”\t”,self.empname,”\t”)
with open (“emp.dat”, “wb”) as f:
e=emp (100, ’pyarungupta’)
pickle.dump(e,f) # Pickling
print(“pickling
of employee”)
with open (“emp.dat”,”rb”) as f:
obj.pickle.load(f) # Unpickling
print(“emp info
after unpickling”)
obj.display()
print(obj)
Simply put, anywhere you need to check if a string matches
or sequence of character(s) a certain pattern and maybe extract certain
information from that pattern.
- Data validation (such as email address or password, Mobile Number)
- Text search
- Pattern Matching
- Search a string (search and match)
- Finding a string (findall)
- Break string into a sub strings (split)
- Replace part of a string (sub)
re module:-regular expressions (Regex) are supported by the re
module
[abc]:- Match either a or b or c.
[^abc]:- Match except a and b and c.
[a-z]:-Match any lowercase alphabet symbols.
[A-Z]:-Match any uppercase alphabet symbols.
[0-9]:- Match any digit; same as [0123456789].
[a-zA-Z0-9]:-Match any of the above
\s:-Match space character
\S:-Match except space character
\d:-Match [0-9] any digit
\D:-Match except digit
\w:-Match any word character (alphanumeric character
[a-zA-Z0-9])
\W:-Match any word character except word (Special character
[^a-zA-Z0-9])
. :- Match every character
except newline
- match (pattern, string)
- full match(pattern, string)
- searchpattern, string()
- findall(pattern, string)
- finditer()
- split(pattern, string, [maxsplit=0])
- sub(pattern, repl, string)
- subn(pattern, repl, string)
- compile(pattern, repl, string)
- escape(string)
Let’s look at them one by one.
match ():- Finds match if it occurs at start of
the string.
checks for a match only at the beginning of the string.
match is much faster than search
Syntax:-re.match(pattern, string)
For example:-
fullmatch():-Match whole string in the regular expression pattern.
Syntax:-re.fullmatch(pattern, string)
search():- matches
the first instance of a pattern in a string, and returns it as
a re match object.
checks for a match anywhere in the string
Syntax:-re. search (pattern, string)
For example:-
findall():- matches all instances of a pattern in a
string and returns them in a list,
Syntax:-re. findall (pattern, string)
For example:-
finditer():-its return an iterator yielding match objects over all non-overlapping matches for the RE pattern in string.
Syntax:-re. finditer (pattern, string)
split():-Split string
by the occurrences of a character or a pattern.
Syntax:-re. split (pattern, string, [maxsplit=0])
For example:-
sub():-search a pattern and replace with a new sub string(Substitution
and replacement)
Syntax:-re. sub (pattern, repl, string )
re.sub(regex,replacement,target of string)
For example:-
subn():- Number of replacement happened.
Syntax:-re. subn (pattern, repl, string )
t=re.subn(regex,replacement,target of string)
subn() is similar to sub() in all ways, except in its way to
providing output. It returns a tuple with count of total of replacement
tuple(result string,number of replacement)
For example:-
compile():- Regex are compiled into pattern
objects, which have methods for various operations such as searching for
pattern matches or performing string substitutions
Syntax:- re. compile (pattern, repl, string)
For example:-
escape():-Its return string with all non-alpha numeric back slashed.
Syntax:- re.escape(string)
For example:-
Python Database Programming (PDB):- it’s very common requirement to save data for the future purpose.
Temporary storage areas:-PVM (python virtual memory)
For Example:- list, tuple, dict.Etc
Permanent storage areas:-
File System:- Best
suitable to store very less amount of info
For Example:-Excel, access
Limitation:-
- Huge data
- No query language support
- Security
- Prevent duplicate data
- Data consistency problem
Then go for next database……………
Database:-
- We can store huge amount of info
- Query language support
- Security is more
- Table duplication
Limitation:-
- Cannot hold very huge amount of info like tera bytes of data.
- Structured data but not for unstructured and semi structured data (XML, Network logs)
Advanced data storage technologies ---Hadoop Big data
Python database Communication(PDBC):-
Standard step to communication with database
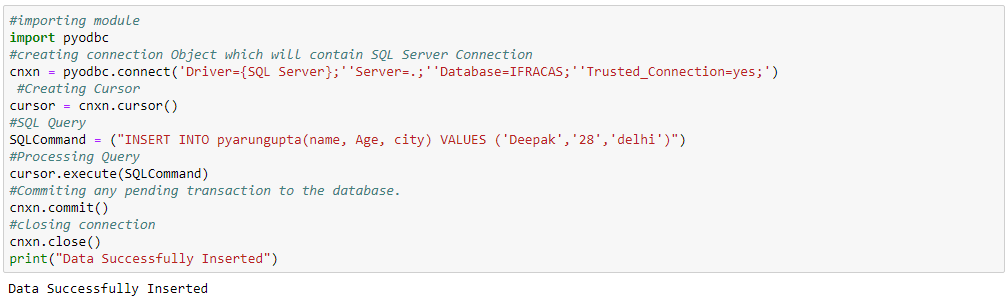
1.Import that database specific module
import pyodbc
2. Establish connection between python program and
database
cnxn = pyodbc.connect('Driver={SQL
Server};' 'Server=.;' 'Database=IFRACAS;' 'Trusted_Connection=yes;')
3.Cursor object
cursor = cnxn.cursor()
4.Execute our SQL query
cursor.execute('SELECT * FROM
pyarungupta')
5.Fetch the results
for row in cursor:
print(row)
6. Commit(), rollback()
7.Cursur.closed()
8.Connection .closed()
Working with SQL database:-
Pip Install pyodbc
Establish the connection between
Python and SQL Server using the pyodbc library
For example:-
import pyodbc
cnxn = pyodbc.connect('Driver={SQL
Server};'
'Server=.;'
'Database=IFRACAS;'
'Trusted_Connection=yes;')
cursor = cnxn.cursor()
cursor.execute('SELECT * FROM
pyarungupta')
for row in cursor:
print(row)
Creating a table named pyarungupta
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[pyarungupta](
[id] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL,
[name] [nchar](10) NULL,
[Age] [nchar](10) NULL,
[city] [nchar](10) NULL
) ON [PRIMARY]
Insert Data To Database:-
And check the database, it
will contain data which you have inserted.
Update In
Database:-
And check the database, it
will contain data which you have Updated.
Delete From
the Database:-
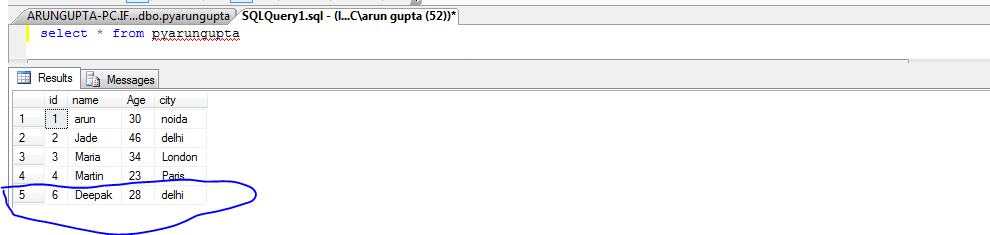
Retrieve Data
from the Database:-
We can retrieve data
from the database by two ways.
- Fetch
one row at a time:- We call fetchone()
method.
- Fetch
all rows: We call fetchall() method.
 Tips & Tricks to write better python:-
Tips & Tricks to write better python:-1.Simplify if statement:-
Verify multiple values, we can
do in the following manner.
The bad way
if m==1 or m==3 or m==5 or m==7:
The good way
if m in [1,3,5,7]:
The bad way
if m==1 or m==3 or m==5 or m==7:
The good way
if m in [1,3,5,7]:
2.Check
the memory usage of an object:-
>>>import sys
>>>x=2
>>>print(sys.getsizeof(x))
14
>>>x=2
>>>print(sys.getsizeof(x))
14
3.Create a
dictionary from two related sequences:-
>>>t1 = (1, 2, 3)
>>>t2 = (10, 20, 30)
>>>print(dict (zip(t1,t2)))
{1: 10, 2: 20, 3: 30}
>>>t2 = (10, 20, 30)
>>>print(dict (zip(t1,t2)))
{1: 10, 2: 20, 3: 30}
4.Transposing
a Matrix:-
>>> mat = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]
>>> zip(*mat)
[(1, 4), (2, 5), (3, 6)]
5.Swap two
numbers with one line of code:-
>>> a=7
>>> b=5
>>> b, a
=a, b
>>> a
5
>>> b
7
6.Print
"arunarunarunarun guptaguptaguptaguptagupta" without using loops:-
>>> print ("arun"*4+'
'+"gupta"*5)
arunarunarunarun
guptaguptaguptaguptagupta
7.Convert it to a single list without using any loops:-
a = [[1,
2], [3, 4], [5, 6]]
Output:- [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
Output:- [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
>>> import itertools
>>>
list(itertools.chain.from_iterable(a))
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
8.Taking a
string input:-
For example "1 2 3 4" and return
[1, 2, 3, 4]
Remember list being returned has integers
in it.
Don't use more than one line of code.
Don't use more than one line of code.
>>>
result = map(lambda x:int(x) ,raw_input().split())
1 2 3 4
>>>
result
[1, 2, 3, 4]


















































Good article for python basics
ReplyDeleteVery good article. It is very useful.
ReplyDeleteThanks for watching
DeleteThanks for watching
ReplyDeleteThanks for watching
ReplyDeleteThanka for giving great info on great blogs. I will definitely will look up the web to find inspirations.
ReplyDeleteNice documents
ReplyDeletethank you to all for watching this blog..
ReplyDeleteplease share your comment & suggestion!!
Nice and knowledgeable article.
ReplyDeleteThanks vijay
ReplyDeleteGood one for python developers....begineer will learn python programming and prototype easily in 5 mins
ReplyDeleteThanks balachandar
ReplyDeleteThank you all for your valuable comments .
ReplyDeleteVery Nice Effort sir these are amazingly good stuff from beginner to advance level.
ReplyDeleteThank you all for your valuable comments .
ReplyDeleteThanks for visiting our blog website.
ReplyDelete